-
2025 CFO Survey Report Series: CFO Priorities for Advanced Technology Adoption
AGA and Guidehouse’s 2025 CFO Survey explores how government financial leaders are navigating AI adoption.…
-
Fall 2025: Celebrating 75 Years of AGA
This issue’s special theme, Celebrating 75 Years of AGA, inspired a variety of interesting and…
-
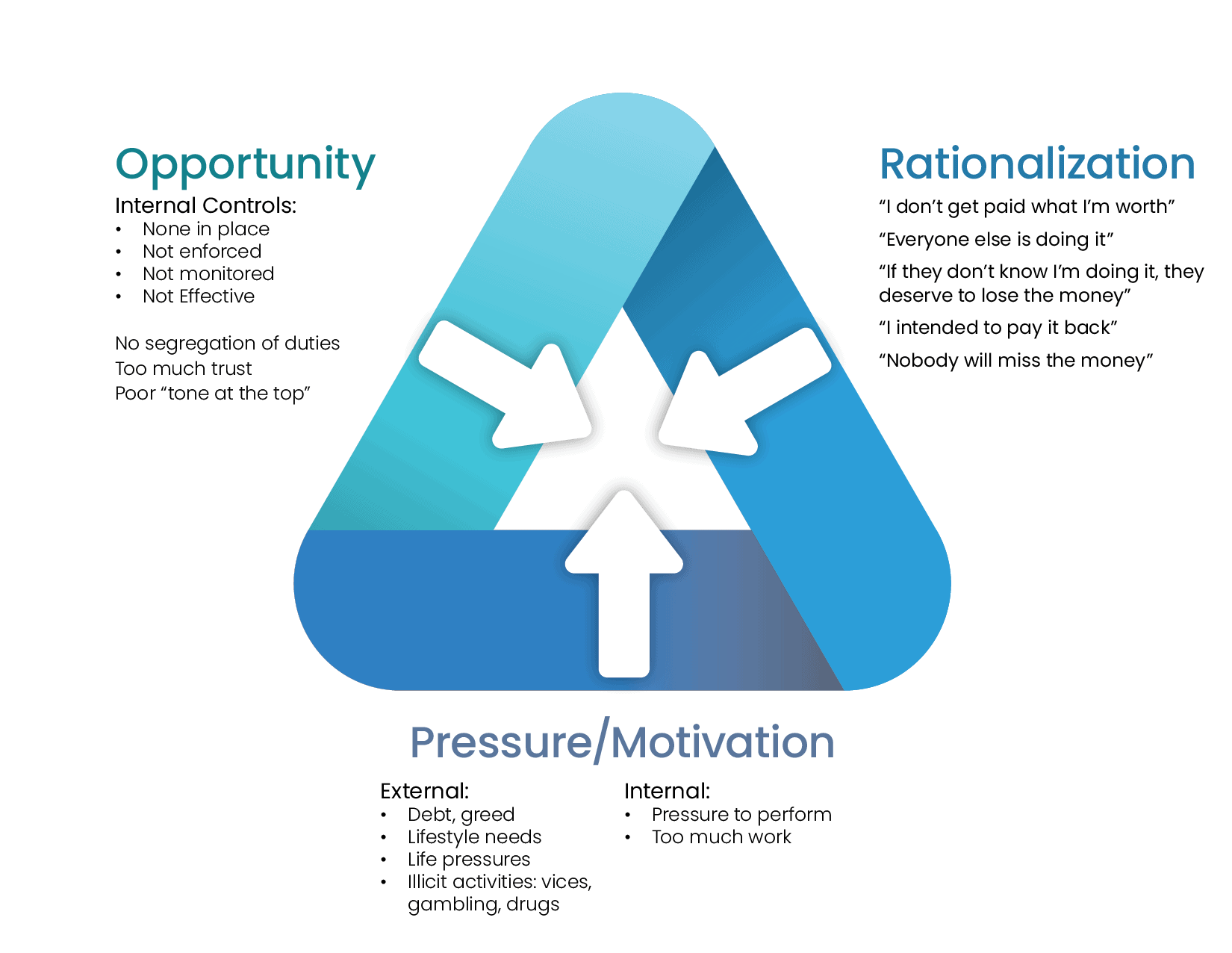
The Fraud Triangle
To fight fraud one must not only realize that it occurs, but also how and…
-
2025 Performance Counts Report
AGA has released its 2025 Performance Counts report, highlighting insights from a critical summit on…
-
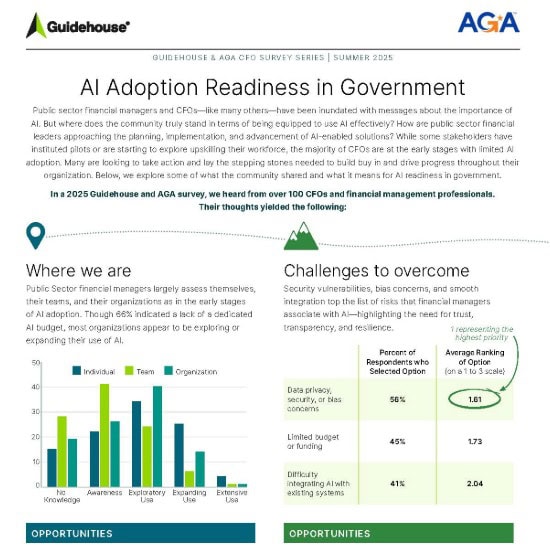
CFO Survey Report 2025
AGA, in collaboration with Guidehouse, introduces the latest edition of its CFO Survey Series, entitled…
-
Summer 2025: The Government’s Fiscal Condition
The summer edition of the Journal of Government Financial Management theme, “The Government’s Fiscal Condition,” inspired a…
-
An Independent View of DOD Challenges from the Vendor Community
This report is the second in a series created by AGA’s Corporate Partner Advisory Group…
-
Spring 2025: Preparing for the Future of Government
With fewer available accountants, how can organizations best attract and retain financial management staff? How…
-
Winter 2025: Calculating the Value of Good Government
Sound leadership and oversight benefits goverment program participants but calculating the value of program management…
-
AGA Research: Driving Project Success Through Organizational Change Management
This report explores how effective change management enhances project outcomes. It offers strategies to integrate…
Become a CGFM
Learn the value and benefits of becoming a CGFM.